What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a bacterial infection that targets the periodontium – the intricate web of tissues and structures that support your teeth. This includes your gums, the underlying bone, and the connecting ligaments. Periodontitis impacts all these periodontal tissues, with the severity of the infection varying based on its stage. Left untreated, it can escalate from an initial stage, often resembling gingivitis, to an advanced phase called periodontosis, resulting in rapid tooth loss.
Understanding Periodontitis: Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of periodontitis should never be ignored, as they inevitably lead to a worsening of the condition and its progression into a chronic state. Here are some telltale signs:
- Gum bleeding
- Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold
- Gum pain and tenderness
- Gum recession
- A sensation of longer teeth
- Tooth mobility
- Shifting teeth
- Persistent bad breath
Overlooking even one of these symptoms can contribute to the development and escalation of periodontitis. If you experience any of these signs, it is essential to consult a specialized dentist for a thorough oral examination.
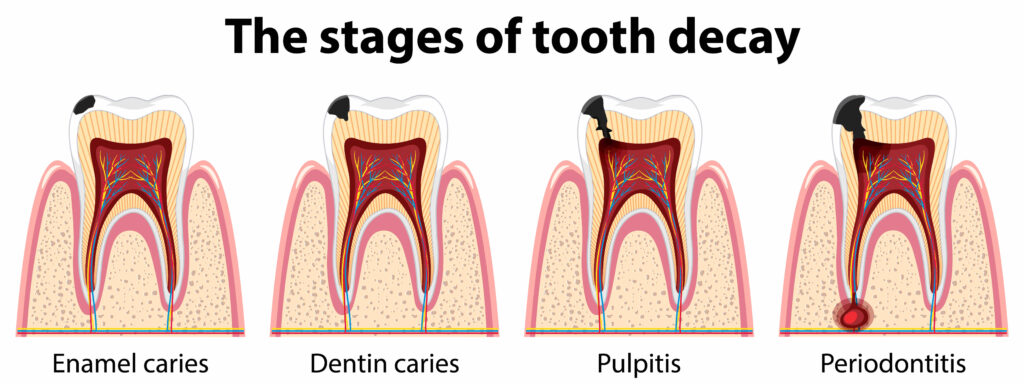
Unmasking the Causes of Periodontitis
The primary causes of periodontitis include:
- Inadequate or ineffective daily oral hygiene
- The buildup of bacterial plaque
- Formation of tartar (calcified plaque)
While various individual factors can contribute, periodontal disease is primarily driven by the absence of proper dental care.
Preventing Periodontitis: Your First Line of Defense
Preventing periodontitis begins in childhood, where the primary symptoms can be mitigated through some straightforward measures:
- Regular professional dental cleanings by a specialized dental professional.
- Adherence to proper daily dental hygiene practices after every meal.
- Vigilance regarding the symptoms of gum disease.
Treating Periodontitis: A Modern Approach
The most modern and effective method for treating periodontitis, as adopted by dental clinics like those in the OdontoSalute network, emphasizes non-surgical approaches, favoring the use of dental microscopes and periodontal lasers. When applied promptly, these tools can lead to the gradual regression of the disease, potentially halting periodontitis altogether. The dental microscope’s precision allows for the treatment of diseased tooth roots without the need for gum surgery. The periodontal laser immediately eliminates pathogenic bacteria in hard-to-reach areas of the periodontium, such as less vascularized spongy tissues and bone. This technique is virtually painless and typically does not require anesthesia. It swiftly halts gum bleeding, closes periodontal pockets, regenerates periodontal tissues, reduces patient discomfort, and minimizes costs associated with traditional surgical procedures.
Periodontitis in Children: Starting Prevention Early
Contrary to common belief, gum disease can affect children and adolescents, with varying levels of severity and the potential for aggressive relapses during growth. To prevent primary symptoms of periodontal disease in children and teenagers, early education is key. Encouraging them from a young age to practice proper and regular daily oral hygiene after each meal and scheduling routine professional oral hygiene sessions at a trusted dental office can make a significant difference.
Painless Periodontitis Treatment
Dental anxiety is a common concern for many. All treatments can be carried out using conscious analgesic sedation, ensuring a relaxed experience. This non-invasive and side-effect-free method involves the administration of analgesic medication via nasal nebulization. It can be used for various dental treatments, reducing pain perception and anxiety levels in patients while leaving them conscious and lucid. Conscious analgesic sedation is suitable for all age groups, including children.

The Cost of Treating Periodontitis
Prevention is a highly effective tool against periodontitis, allowing for the containment of the issue before it even arises. A comprehensive check-up and patient history assessment by a specialized professional are the first steps in evaluating specialized treatments and potential treatment plans.
In conclusion
Periodontitis is a serious oral condition that, if left untreated, can have significant consequences. Prevention and early intervention are essential for managing and potentially stopping the disease’s progression. If you experience any gum disease symptoms or have concerns about your oral health, consult with a specialized dentist for a thorough evaluation.

